Parts
of speech in English means the kinds
of words or class of word . Called part of speech or part of
sentences (remember, basically sentences are sentences in a language that is
spoken, not written) because of these
words is a system that is needed to form a sentence, regardless of what duties or function of each. So, the word
are “basic ingredients” in a” building” the sentence, not “function” words in
the sentence. Why is that? Because a
word can have several (more then one) function in the sentence.
Ada
9 bagian dalam Part of speech, yaitu:
1. VERB
(KATA KERJA)
Verb: be, have, do, like, work, sing, run, kick, can, must,
etc.
Example
: I write a letter now.
If
adv of time was changed, the verb will change too.
Example;
I
wrote a letter yesterday.
Types
of Verbs :
Regular : Love – Loved – Loved
Irregular : Go – Went – Gone
- Transitive >< Intransitive
Transitive (need object) : They eat some apples everyday
Intransitive (not need object) : Women sleep
Finite >< Nonfinite
Perubahan verb dikarenakan waktu,
E xample : I want to go home now.
I wanted to go home yesterday
Want > wanted (finite)
-Auxially Verb
-Linking Verb
B. NOUN (KATA BENDA)
benda-benda yang pasti dan memiliki bentuk.
Example : chair, table, book, pen, pencil, door, window, etc.
benda yang abstrak/tidak memiliki bentuk yang kasat mata.
Example : friendship, happiness, health, beauty, freedom, etc
berisi nama-nama hari, nama-nama bulan, nama-nama tempat.
Example : sunday, monday, june, april, john, jane, jack, etc.
Example : fish, man, woman, teacher, table, car, book, door, etc
Benda-benda yang masih dapat dihitung.
Example :
Singular: a book (kata benda tunggal)
Plural: Three book (lebih dari 1 (jamak))
f. Uncountable Noun
Benda-benda yang tidak dapat dihitung.
Example : sugar, sand, hair, money, etc.
Berisi benda-benda material alam.
Example : gold, rock, etc
Adjective
is a word used to limit ("Modify") or describe nouns (Noun) or a pronoun
(Pronoun). The word "Modify" means "change". To change a
word means to change the meaning of the word by making its meaning more
clearly.
To
determine whether a word is an adjective that serves to explain or change the
meaning of a noun or pronoun can be known by answering the following questions:
What Kind?, Which one?, There are how many?
Example:
Good, bad, smart, lazy, etc
A blue dress That flower Four times
A false note Third base Several girls
A rich lawyer The broken bone Each player
A short one The other one Some others
A false note Third base Several girls
A rich lawyer The broken bone Each player
A short one The other one Some others
Adverb is use to give adverb of time, adverb of place and adverb of manner in the sentence.
a. Adverb of Time
Example : now, yesterday, tomorrow, tonight, etc
b. Adverb of Place
Example : here, there, outside, etc
c. Adverb of Manner
Example : slowly, easily, badly, etc
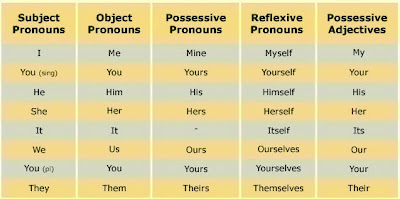
Pronoun is use for change the noun in the sentence.
I, we you, they, he, she, it, me, us, you, him, them, her, it, my, our, your, his, their, her, its)
Example : Anderson said to Jane that Anderson Would invite Jane to attend the party.
Become : Anderson said to Jane that he Would invite her to attend the party.
- Prossesive Pronoun Type I :
My pen
Her house
- Prossesives Pronoun Type II :
Noun + Prossesives Pronoun
The pen is mine
The houses are their
- Example gabungan
My pen in her houses
My pencil in their houses
Some one, every one, no one, every thing, every body, any one, any thing.
3. nterogatives Pronoun
Who, which, whom, what.
4. Reflexive Pronoun
My self, our self, your selves, him self, them selves.
5. Pemanstrative Pronoun
This, That.
6. Relatif Pronoun
Who, that.
7. Reciprocal Pronoun
Each other.
A preposition or kata depan is a word used to indicate the relationship between a noun or a pronoun. Relationship between them can be seen in a series of sentences below:
Example:
- I go to the market
- He go to the market after me.
Conjunction is a word that is syntactically connecting to a larger constituency and also state the semantic relationship between them. A conjuction is a liason position has been fixed for one or two related elements, which distinguishes it from constituens like kongjuctive adverv in English.
In general, a conjuction is grammatical elements that do not change, and may or may not be standing where the elements in the sentence combined (and, but, when).
Example:
- I like coffee and tea, but I don’t like juice
- When I go to the market, I see her
- Budi and ani are student.
- I like green and red colours.
- I like coffee, but my brother like tea
- Jack and john are friend.
An interjection is a word or phrase that indicates emotion or surprise which has no grammatical relation to any words that are part of the sentence. Better avoid using this in formal writing except in direct quotes. In most dictionaries use the cutting down of the "interunction”." Means "interjection." Or "kata seru”. For instance the word:
Ouch, Oh my god, Wow, Ugh, excellent, well, great. etc.
Example:
- Wow, You make me surprised!!
- Excellent, you Did it!!
- Oh my god, you finished it!!
- Ugh, great!!









ini yang saya butuhkan, izin copast gan buat tugas kampus.
ReplyDeleteYup, silahkan gan.. Copast aj..
Deletewow!!pas banget buat tugas kampus,
ReplyDeletekeep blogging ya gan!!
yups,
ReplyDeleteterimakasih atas kunjungannya sist..
kerenn
ReplyDeletethanks for visiting theenglishcamp :)
Delete